20 Year History of RMSCC
The work of the RMSCC has been a progression of innovative idea’s put to practice, spanning over 20 years of progress.
State of the industry then:
The work of the RMSCC was born out of the need to provide evidence of food safety and to enable traceability. Some major systems in Australia's traceability systems had been in place for a while now. Property Identification Codes were developed back in the 1960's. The National Vendor Declaration came about in 1996. However, the systems were struggling to keep up with the amount of information they had to process. Barcoding standards were developed and implemented by the RMSCC as a way for livestock vendors, meat processors, and retailers to utilise this information and more, enabling a more robust traceability solution.
State of the industry now:
These days, businesses in other sectors of the meat industry have begun to adopt these data standards, such as in the export sector. Supported by online tools such as Meat Messaging, the RMSCC has continued to keep businesses in Australia’s meat industry communicating their information globally.
State of the Industry in the Future:
The RMSCC is looking to a future that would enable all businesses across the meat industry's sectors to communicate with each other. The focus is on developing fit for purpose, voluntary standards that allow interoperability within and between the industry. We are establishing an information standards development process that will the community closer to the standards they use, while continuing to help the industry grow and connect.
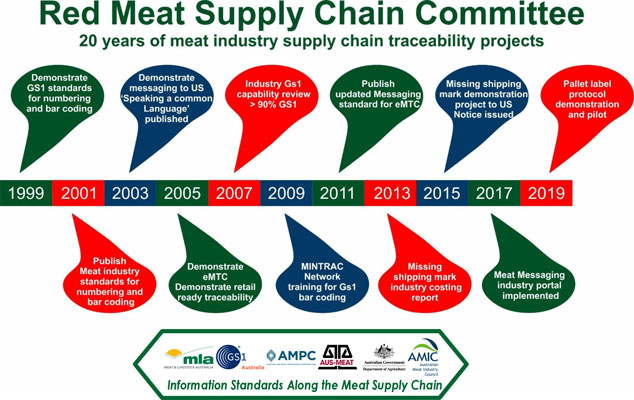
- 1999 – Demonstrate GS1 standards for numbering and barcoding
The RMSCC worked in conjunction with industry representatives to prove that barcoding could be a solution to traceability in the red meat industry. - 2001 – Publish Meat Industry standards for numbering and barcoding.
The work of previous case studies was adapted into a Guideline to help businesses implement this tried and true method for traceability. - 2003 - Demonstrate messaging to US; "Speaking a Common Language" CD published.
A case study was published demonstrating the use of barcoding standards applied to red meat exports to the US.
Meat and Livestock Australia published a CD version of the Guidelines, which was used in national accreditation courses. - 2005 – Demonstrate eMTC; Demonstrate retail ready traceability.
Traceability solutions were expanded to include the development of the eMTC, an electronic version of the Meat Transfer Certificate. - 2007 – Industry GS1 capability review; >90% GS1.
The meat industry's exporters to the US were surveyed on their readiness to implement global data standards. Majority of meat exporters to the US were found to be either already implementing or capable of implementing global data standard, with approximately 90% of exported product to the US using GS1 barcoding standards. The focus began on closing the gap and expanding to other information standards. - 2009 – MINTRAC Network training for GS1 barcoding.
The National Meat Industry Training Advisory Council began teaching GS1 barcoding standards to the industry. - 2011 – Publish updated messaging standard for eMTC.
The RMSCC completes work on bringing the eMTC standard, updating the standard with lessons learnt from plant and system vendor case studies. - 2013 – Missing shipping mark industry costing report.
The RMSCC finalises a report estimating the cost-benefits of the meat export implementing a single source, global data standard with the US to correct problems with missing shipping marks. - 2015 – Missing shipping mark demonstration project to US; Notice issued.
A proof of concept case study that used the Meat Messaging portal to assist US authorities verify carton containers missing shipping marks. - 2017 – Meat Messaging industry portal implemented.
Meat Messaging, an online tool to assist organisations implement GS1 standards that meet regulatory compliance, is launched. - 2019 – Pallet label protocol demonstration and pilot.
A case study demonstrates the benefits that exporters can realise if they use global data standards with the assistance of Meat Messaging.